INBRIJA®—the only inhaled levodopa for on-demand use in patients taking CD/LD.21
Here are 2 ways to prescribe INBRIJA*:
ePrescribe INBRIJA in 2 simple steps

1-949-524-3566
(Recommended)
NCPDP: 5664417
NPI: 1871002485
Address:
361 Hospital Rd., Ste 425
Newport Beach, CA 92663


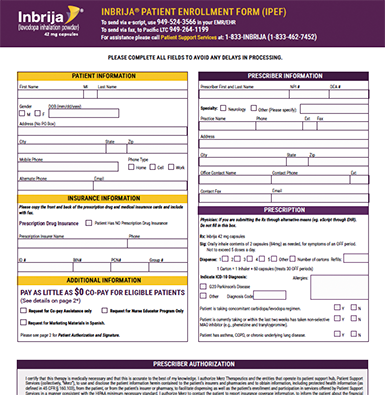
Complete the Patient Enrollment Form
(Formerly known as Prescription Request Form)
FILL OUT FORM

Download and fill out a Patient Enrollment Form
FAX

Fax completed form to 1-949-264-1199
If you do not have access to a fax machine, call us at 1-833-INBRIJA (1-833-462-7452).
* |
Available at a variety of specialty pharmacies nationwide. |
† |
You may receive a phone call from an INBRIJA patient support specialist if additional information is required to initiate prior authorization. |
‡ |
Standard text and data rates may apply. |
|
EMR, electronic medical record. |
INBRIJA prescription and patient support
INBRIJA prescription process
Submit eRx or Patient Enrollment Form (iPEF)
To Pacific LTC Pharmacy via e-script, use 1-949-524-3566 in your EMR/EHR
Patient support services
Benefits Investigation, Prior Authorization, and Appeals Support
Savings and Financial Assistance Eligibility Determined
Nurse Educator Inhaler Training and Support
Specialty§ pharmacy
Patient
§ |
Available at a variety of specialty pharmacies nationwide. |
|
EHR, electronic health record. |


 print instructions
print instructions